In mining operations, primary crushing is the choke point of the entire process. Choosing the right primary crusher is a crucial step in determining subsequent production efficiency, operating costs, and the final return on investment. Among the many options, jaw crushers and gyratory crushers are the two most mainstream solutions. However, this battle of the titans has no absolute winner, only the choice best suited to your specific working conditions.
Gyratory Crusher PDF , Download ↓↓↓
This article will provide an in-depth comparison of jaw crushers and gyratory crushers, from their working principles to applicable scenarios, offering you a clear selection framework.
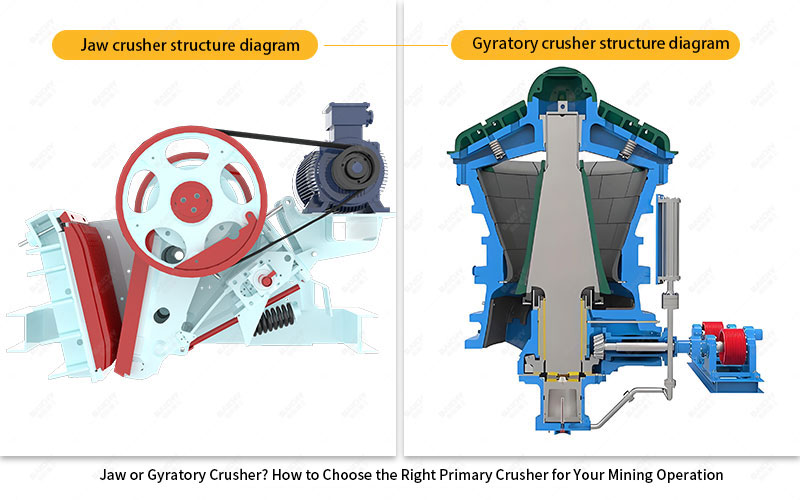
I. Core Showdown: Working Principles and Structural Differences
To make the right choice, you first need to understand how they work.
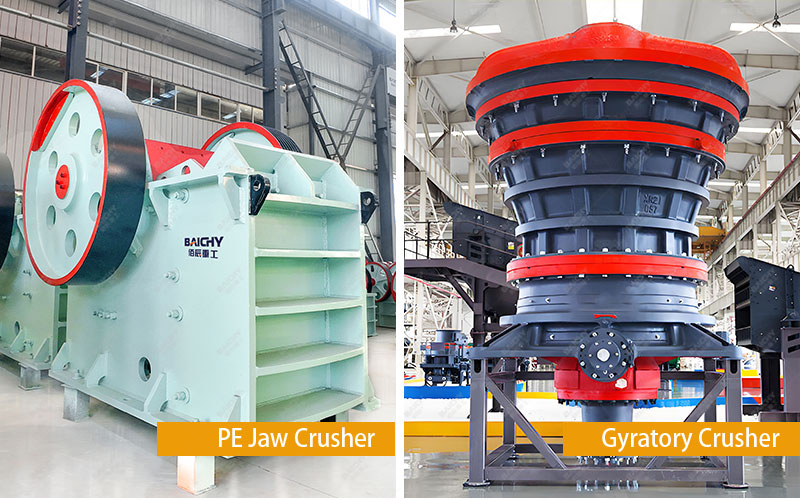
• Jaw Crusher: Uses the reciprocating squeezing motion between the moving jaw and the stationary jaw to crush materials. Its working principle is simple and intuitive, similar to an animal's chewing action. This intermittent working method makes its structure relatively simple and compact.
◦ Advantages: Simple structure, low height, lower investment cost, and convenient maintenance.
• Disadvantages: Jaw Crusher: Intermittent operation, relatively low capacity, slightly poorer product particle size uniformity, prone to producing flaky products.
• Gyratory Crusher: The core component is a fixed concave outer casing and an internally rotating eccentric cone. Material is continuously squeezed, bent, and crushed between the cone and the casing.
• Advantages: Continuous operation, extremely high capacity per unit of power consumption, large throughput, and more uniform product particle size.
• Disadvantages: Complex structure, large and heavy machine, high initial investment, and more specialized installation and maintenance requirements.
II. Key Indicator Comparison: Helping You Make Data-Driven Decisions
The table below visually illustrates the differences in key performance characteristics between the two crushers.
| Comparison Indicators | Jaw Crusher | Gyratory Crusher | Selection Insights |
| Capacity and Power Consumption | Intermittent operation, relatively low capacity, average energy efficiency | Continuous operation, extremely high capacity, lower power consumption per ton of ore | For large-scale, high-efficiency production, choose the gyratory type |
| Feed Size | Can handle larger lumpy materials, but is relatively limited | Capable of handling very large raw materials with a larger feed opening | For extremely large ore, a gyratory type is the preferred choice |
| Product Size | Wide particle size distribution, with more flaky material | More uniform particle size, with more cubic particles, beneficial for subsequent crushing | For strict requirements on product particle shape, a gyratory type is superior. |
| Installation and Maintenance | Compact structure, low height, flexible installation, and simple maintenance | Large machine height, requires a solid foundation, complex maintenance, and long downtime | Jaw type is preferred for sites with limited space or lack of large lifting equipment. |
| Investment Cost | Lower initial purchase and installation costs | Very high initial investment | Jaw type is more economical for small to medium-sized mines with tight budgets. |
| Moist/Sticky Materials | Poor adaptability to sticky materials, prone to clogging | Stronger ability to handle sticky or moist materials | Gyratory type is more reliable when materials have high moisture content and high viscosity. |
III. How to Choose? Answer These Key Questions
Now, please answer the following questions based on your project's specific circumstances:
1. What is your target daily throughput?
◦ If > 10,000 tons: The high capacity and low cost per ton of ore offered by gyratory crushers will be very significant.
◦ If < 5,000 tons: Jaw crushers are likely a more cost-effective option.
2. What is the maximum particle size of your ore? What are the material characteristics?
◦ If the ore is extremely large (>1 meter) or very hard: Gyratory crushers are experts at handling large materials.
◦ If the material is sticky or has a high moisture content: Gyratory crushers are preferred.
◦ If the material is highly abrasive: Replacing the wear parts (jaw plates) of a jaw crusher may be quicker and less costly.
3. What are your site and mobility requirements?
◦ Fixed, long-term mining: Both are suitable, but gyratory crushers are better suited for large, fixed plants.
◦ Conditions requiring semi-mobile or frequent relocation: Jaw crushers are more widely used in semi-mobile crushing plants due to their lower overall height and weight.
4. What is your budget?
◦ Limited capital budget: Jaw crushers can significantly reduce upfront investment.
◦ Focus on long-term operating costs (OPEX): Although gyratory crushers have a higher initial investment, their extremely high efficiency and low power consumption per ton of ore will bring considerable returns in the long run.
IV. Conclusion and Final Recommendations
• Choose a jaw crusher if: Your mine is small to medium-sized, has a limited budget, limited space, or has high requirements for production flexibility (such as semi-mobile). It is a reliable, economical, and easy-to-maintain all-rounder.
• Choose a gyratory crusher if: Your goal is large-scale, high-efficiency continuous production, handling large volumes of ore with large block sizes, and you are willing to make upfront investments for higher production efficiency and lower long-term operating costs. It is the king of efficiency for large-scale production.
There is no best equipment, only the most suitable choice. Best practice often involves a comprehensive assessment of your needs, consulting with professional equipment suppliers for on-site surveys and simulations, to make the wisest investment decisions and ensure your primary crushing stage becomes a powerful engine for the entire mining operation.