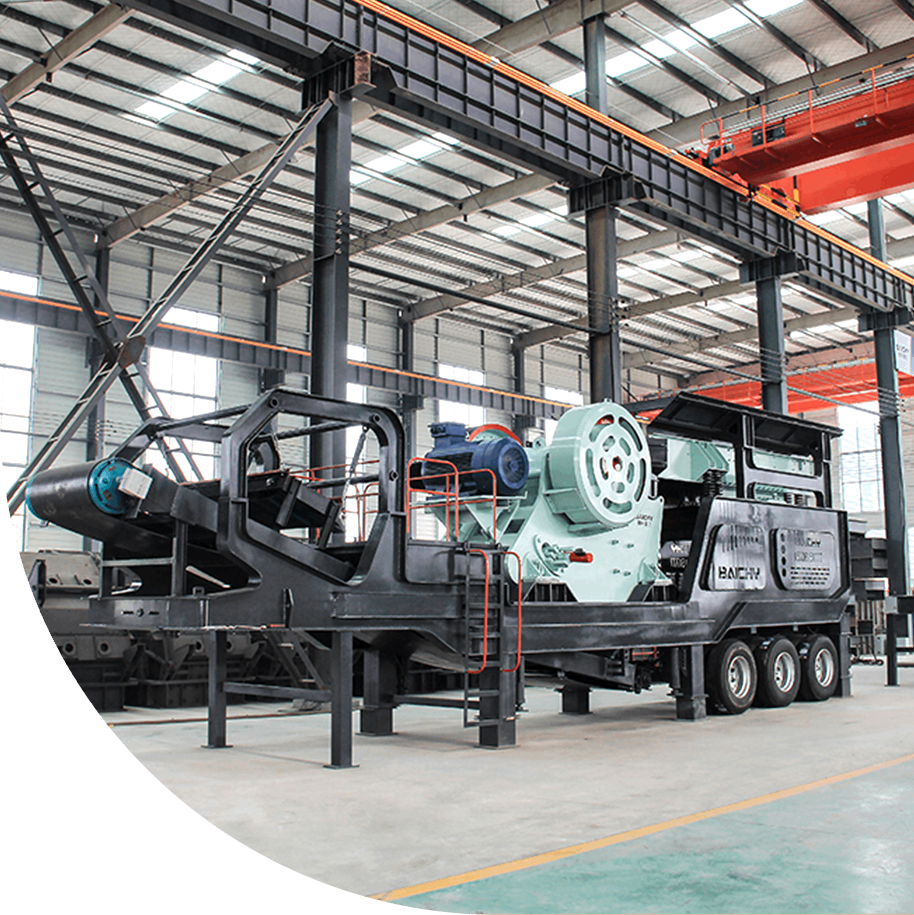
The cement ball mill is the core grinding equipment of the cement production line. It is mainly used to grind cement clinker, gypsum, and mixed materials (such as slag, fly ash, etc.) to the required fineness to meet the quality requirements of different grades of cement. The equipment has the characteristics of high efficiency and energy saving, stable operation, and strong adaptability, and is widely used in cement, building materials, metallurgy, chemical industry, and other industries.
• Applicable materials: cement clinker, slag, fly ash, gypsum, limestone, etc.
• Grinding method: dry/wet grinding (the cement industry mainly uses the dry method).
• Typical capacity: 20-200 tons/hour (depending on specifications and processes).
• Fineness range: adjustable 300-450 m²/kg (specific surface area).

Cement production line site

Cement grinding equipment

Ball mill lining

Ball mill reducer
1. Cement clinker grinding: Grind cement clinker with gypsum and mixed materials (such as slag, fly ash, volcanic ash, etc.) to the specified fineness (specific surface area 300-450 m²/kg); suitable for small cement plants, simple process, but high energy consumption.
2. Slag micro powder production: Grind blast furnace slag into slag micro powder (specific surface area ≥420 m²/kg) as a cement admixture or concrete additive; improve cement strength, reduce hydration heat, reduce clinker consumption, and reduce production costs.
3. Composite cement production: Mix and grind clinker, slag, fly ash, limestone, etc. to produce cement of different grades (such as P·C32.5, P·O42.5).
1. Limestone grinding: production of limestone powder for construction, used as a concrete admixture or desulfurizer; fineness requirement 80-200 mesh (0.075-0.2mm).
2. Gypsum grinding: natural or desulfurized gypsum for cement retarder or gypsum board production.
3. Ceramic raw material processing: grinding quartz, feldspar, clay, and other ceramic raw materials to improve sintering performance.
1. Slag treatment: grinding blast furnace slag and steel slag for cement admixture or roadbed material.
2. Ore dressing plant tailings treatment: fine grinding tailings to improve the metal recovery rate or prepare building materials raw materials.
1. Non-metallic mineral grinding: processing barite, talc, bentonite, etc., used for coatings, plastics, rubber fillers; fineness requirements 400-2500 mesh (ultra-fine grinding requires classification equipment).
2. Coal powder preparation: grinding coal for combustion in power plant boilers or cement kilns.
• The use of scientifically graded grinding bodies and closed-circuit grinding technology improves grinding efficiency by 20-30%;
• Innovative energy-saving design (frequency conversion drive + high-efficiency lining) reduces power consumption by 15-30%, and the power consumption per ton of cement is ≤ 30 kWh.
• It can handle a variety of materials such as cement clinker, slag, fly ash, etc..
• By adjusting the powder selector and grinding body, the fineness of the finished product can be accurately controlled at 300-500m²/kg.
• Heavy-duty bearings + gear transmission ensure smooth operation, low failure rate, and operation rate ≥95%;
• Modular quick-disassembly design makes the replacement of wearing parts more efficient and minimizes downtime.
• Equipped with a high-efficiency dust removal system, dust emission ≤30mg/m³, which is better than the national standard;
• Optional intelligent control system, real-time monitoring of key parameters, and support for unmanned operation.

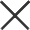
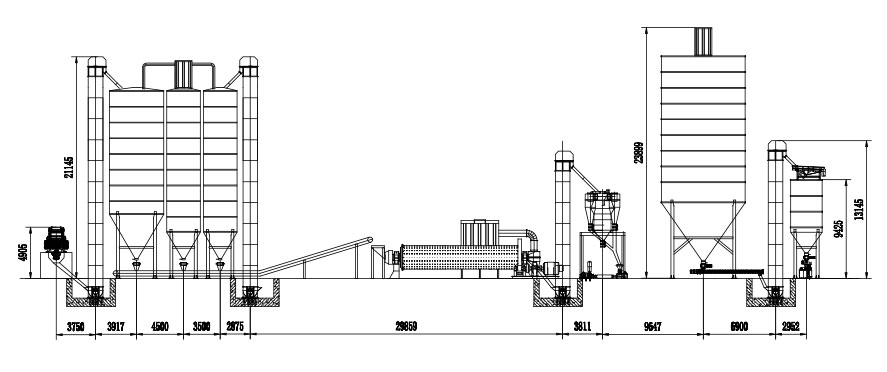
Limestone is more commonly used in the cement preparation process, but the mined limestone generally has larger particle sizes and needs to be crushed. Generally speaking, processing limestone into cement requires the preparation and homogenization of raw materials, the preparation of pulverized coal, the calcination of clinker, and the grinding of cement. stage.
1. Preparation and homogenization of raw meal: natural limestone, clay, and exotic raw materials are crushed by a jaw crusher and mixed in a certain proportion, and then ground by a ball mill to prepare raw meal with appropriate composition and uniform quality;
2. Pulverized coal preparation: The coal required for calcining cement raw materials must be prepared into pulverized coal to provide the particle size required for pulverized coal combustion to facilitate full combustion and obtain sufficient combustion reaction capacity. In this process, pulverized coal can be directly added, and equipment such as jaw crushers and ball mills will be used for processing.
3. Clinker calcination: Put the lime raw material in the rotary kiln and calcine it until it is partially melted to obtain lime clinker.
4. Cement grinding: that is, adding an appropriate amount of gypsum, mixed materials or additives to the clinker to grind it into cement, and then package it for shipment.

| Model | Capacity(t/h) | Rotate speed(r/min) | Grinding Balls(t) | Motor Power(kw) | Gear box | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Speed Ratio | |||||
| Ф1.2x4.5 | 1.6-5.8 | 30.3 | 5 | 55 | ZD30 | 4.5 |
| Ф1.5x5.7 | 3.5-6 | 26.34 | 11 | 130 | ZD40 | 4 |
| Ф1.83x6.4 | 6.5-15 | 23.9 | 21 | 210 | ZD60 | 4.5 |
| Ф1.83x7 | 7.5-17 | 24.5 | 23 | 245 | ZD60 | 4.5 |
| Ф2.2x6.5 | 14-20 | 21.4 | 31 | 280 | ZD70 | 5 |
| Ф2.4x7 | 17-28 | 20.4 | 39 | 380 | ZD80 | 5 |
| Ф2.4x8 | 20-35 | 20.3 | 42 | 570 | ZD80 | 5 |
| Ф2.4x12 | 35-45 | 20 | 63 | 800 | MBY710 | 6.3 |
| Ф2.4x13 | 35-38 | 19.4 | 68 | 800 | MBY710 | 6.3 |
| Ф2.6x13 | 40-55 | 19.5 | 82 | 1000 | JDX800 | 6.3 |
| Ф3x9 | 50-55 | 18.34 | 78 | 1000 | JDX800 | 6.3 |
| Ф3.2x9 | 60-70 | 17.6 | 95 | 1250 | MBY900 | 7.1 |
| Ф3.5x11 | 75-85 | 16.8 | 150 | 1250 | JDX900 | 5.84 |
| Ф3.8x12 | 85-110 | 17 | 175 | 1600 | MBY800 | 5.6 |
| Ф4.6x10+3.5 | 180-210 | 15 | 278 | 3550 | JQS3500 | 15.1 |
| Comparison items | Cement ball mill | Traditional Raymond mill/vertical mill |
| Grinding efficiency | High (closed-circuit system) | Medium (relying on classifier) |
| Energy consumption | Low (below 30kWh/t) | High (35-45kWh/t) |
| Material adaptability | Strong (both hard and soft materials) | Limited (hard materials are prone to high wear) |
| Maintenance cost | Low (liner life 2-3 years) | High (frequent roller sleeve replacement) |
Optimize grading: Rationally match steel balls of different diameters (such as Φ60mm+Φ40mm+Φ20mm)
Closed-circuit transformation: Install a high-efficiency powder selector (such as O-Sepa), and control the circulating load at 100%-150%
Variable frequency speed regulation: Adjust the cylinder speed according to the material characteristics
Regular maintenance: Check the wear of the liner and the lubrication status of the bearings
Problem 1: Sudden drop in output
→ Check: steel ball loss, blockage of the partition plate, and whether the moisture content of the material is too high
Problem 2: Bearing temperature is too high (>70℃)
→ Check: lubricating oil volume, cooling system, and whether the bearing is damaged
Problem 3: Abnormal vibration/noise
→ Check: loose anchor bolts, poor gear meshing, and cylinder deformation
Material: high chromium alloy (best wear resistance), low chromium cast iron, forged steel
• Coarse grinding chamber: large balls (Φ60-100mm) account for 40%-50%
• Fine grinding chamber: small balls (Φ20-40mm) account for 60%-70%
• Replenishment cycle: Steel balls need to be added every 500-800 hours of operation
Cylinder:15-20 years (replace the liner regularly)
Liner: 1-3 years (high chromium liner has a longer life)
Gear: 8-10 years (regular lubrication and maintenance are required)
If you need further information,please fill in your questions and comments in the form below.
Representatives from Baichy machinery will be back to you within the hour,thanking you for your support to Baichy machinery