An efficient gold beneficiation plant is a crucial bridge connecting natural ore and brilliant gold. Its core objective is to maximize gold recovery while controlling operating costs. So, what exactly constitutes a standard and efficient gold beneficiation process? This article will provide an in-depth analysis of several mainstream gold beneficiation technologies.

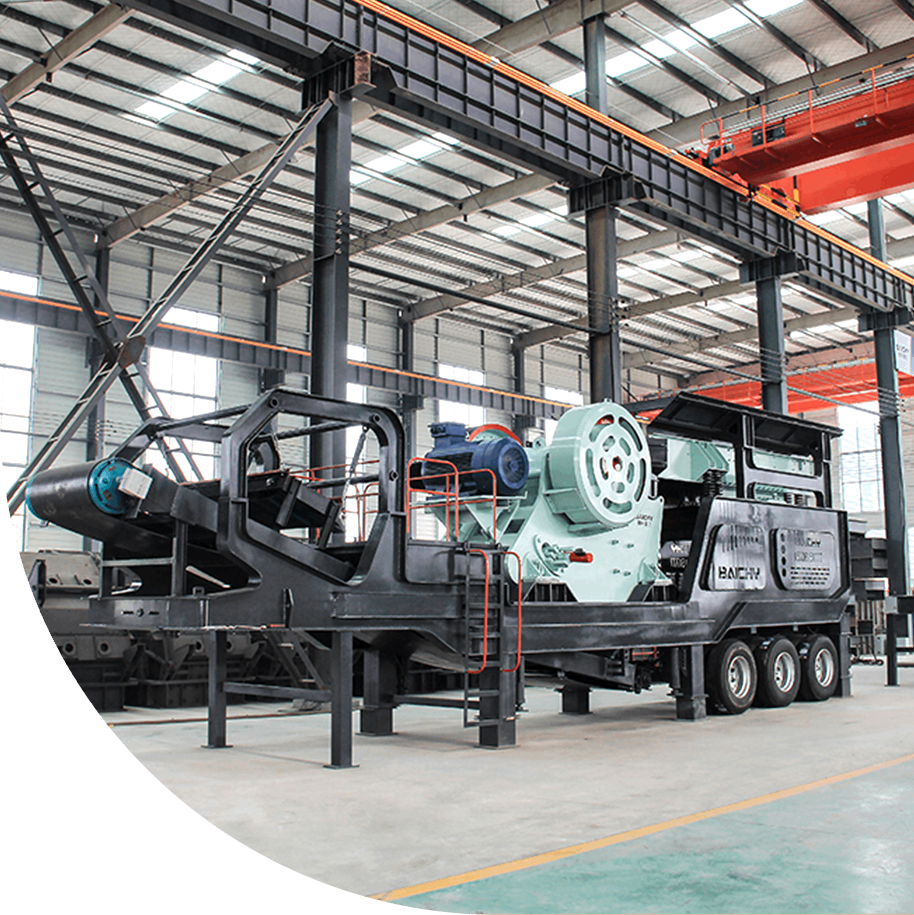
I. Pre-Beneficiation Preparation: Crushing and Grinding
Regardless of the subsequent processes used, all gold ore must first undergo crushing and grinding stages. The purpose is to pulverize large pieces of ore to a suitable particle size for beneficiation, allowing the gold minerals to be fully liberated.
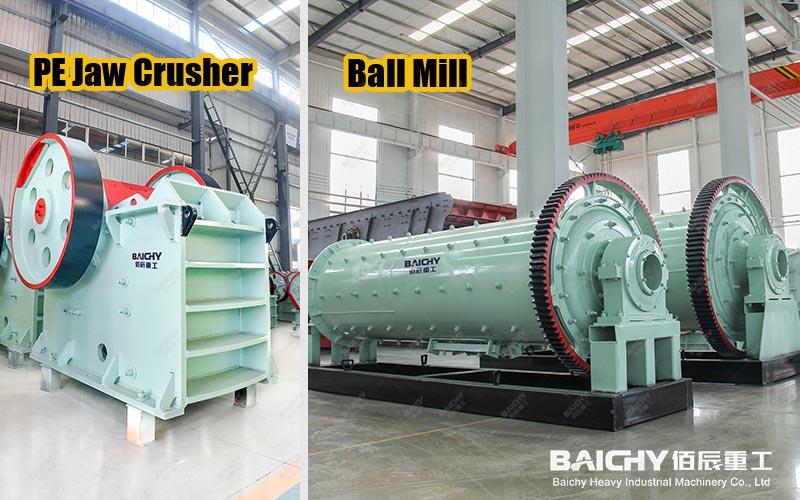
1. Crushing: Typically, a two- or three-stage crushing process (such as a jaw crusher + cone crusher) is used to crush the raw ore to the millimeter level.
2. Grinding: In a ball mill or rod mill, the ore is further ground into powder (typically less than 0.1 mm) with water and steel balls. This process creates the necessary conditions for subsequent beneficiation operations.
II. Core Beneficiation Process: How to Efficiently Recover Gold?
Gold ore beneficiation plants employ various separation methods based on the physical and chemical properties of the gold ore (such as grain size and co-occurrence relationships). These are mainly pided into physical methods (gravity separation) and physicochemical methods (flotation, cyanidation).
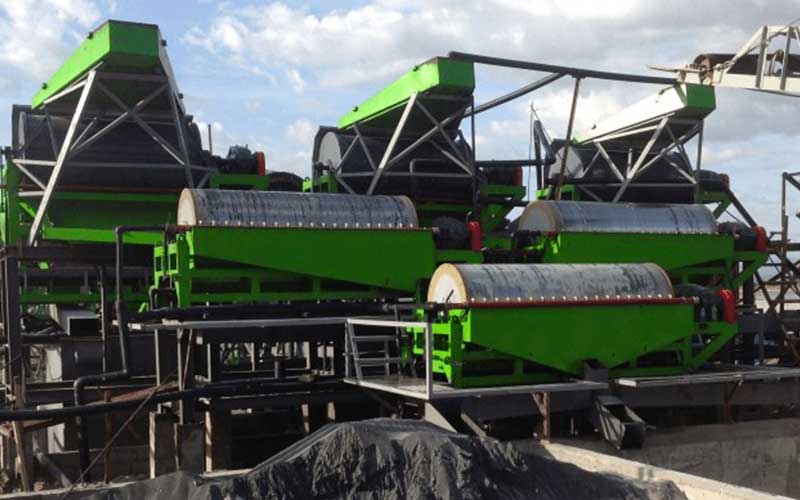
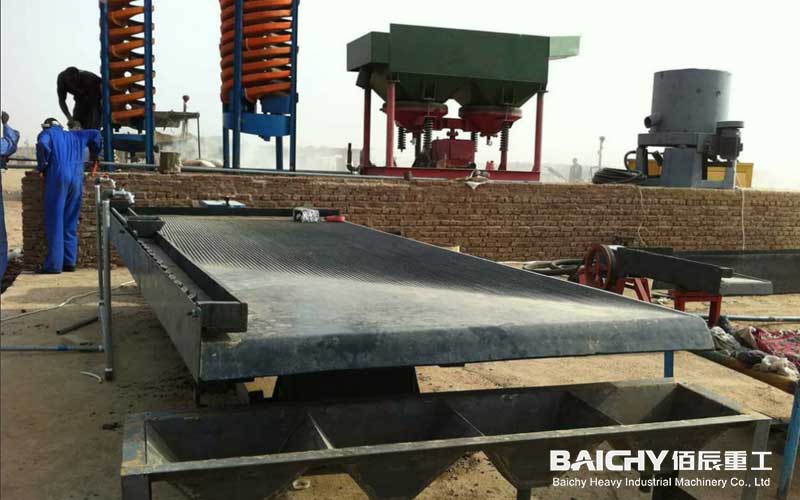
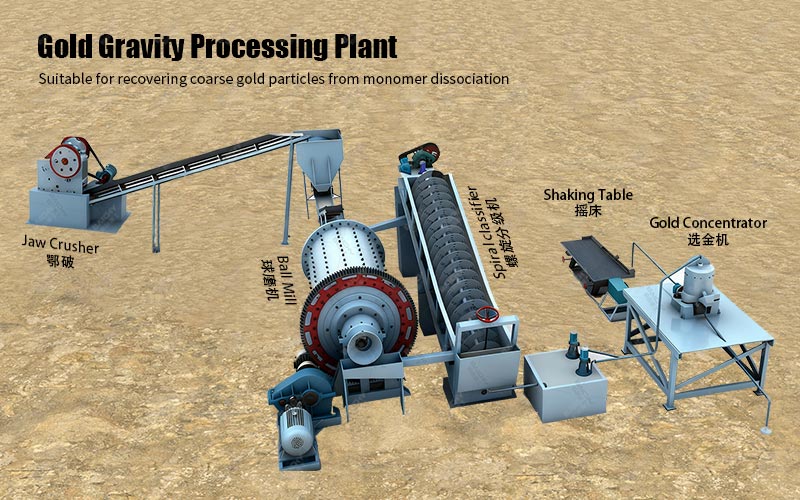
1. Gold Gravity Separation
• Principle: Utilizing the significant difference in specific gravity between gold and other gangue minerals, separation is achieved under the action of water flow and mechanical forces. Gold has a much higher specific gravity than ordinary gangue minerals, thus easily settling and being recovered.
• Applicable Ore: Particularly suitable for coarse-grained placer gold or liberated gold in vein gold deposits.
• Commonly Used Equipment: Nelson centrifuges, jigs, shaking tables, etc. Gold gravity separation is often used as a pretreatment method to recover coarse gold particles in advance, effectively reducing the load on subsequent processes and losses due to leakage.
2. Gold Flotation Technology
• Principle: Utilizing the hydrophobic nature of the physicochemical properties of gold mineral surfaces, flotation reagents are added to cause finely disseminated gold minerals to adhere to air bubbles. These bubbles rise to the surface of the slurry, forming a froth layer, which is then scraped off and recovered.
• Applicable Ores: Commonly used for processing gold-bearing sulfide ores (such as those associated with pyrite and arsenopyrite), or complex ores that are difficult to directly cyanide. Gold flotation technology can yield high-grade gold concentrate, facilitating transportation or subsequent smelting.
• Process: Typically includes roughing, scavenging, and multiple cleaning stages.
3. Gold Cyanide Leaching Process (Mainstream Method)
This is currently the most widely used and economical method globally for processing fine-grained disseminated gold rock ores, with extremely high recovery rates.
• Principle: A dilute sodium cyanide (or potassium cyanide) solution reacts chemically with gold under aerobic conditions to form a soluble gold-cyanide complex, dissolving the gold from the solid ore into the solution.
• Core Process - Carbon-In-Pulp (CIP) / Carbon-Leach-In-Pulp (CIL):
◦ Leaching: In a leaching tank, finely ground ore slurry is thoroughly mixed and reacted with a cyanide solution.
◦ Adsorption: Activated carbon is added to the ore slurry (added after leaching in CIP, and simultaneously in CIL). The activated carbon efficiently adsorbs the gold-cyanide complex in the solution.
◦ Desorption and Electrolysis: The gold-loaded carbon is sent to a desorption electrolysis system to desorb the gold from the activated carbon, and then electrolytically deposited to obtain gold mud.
◦ Smelting: Finally, the gold mud is smelted and purified to obtain the final product—alloyed gold ingots.
Modern gold mine beneficiation plants often employ combined processes, such as gravity separation-flotation-cyanidation or flotation-concentrate cyanidation, to maximize recovery.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Best Process for Your Gold Mine?
There is no one-size-fits-all solution. The optimal gold mine beneficiation process depends on your ore properties (lode gold/placer gold, oxide/sulfide ore, gold distribution characteristics), investment budget, and production scale (large-scale gold mine beneficiation plants have vastly different design approaches than small-scale ones).
Choosing an experienced partner is key to success. Baichy, as a professional gold mine beneficiation equipment and technology service provider, offers comprehensive services from beneficiation trials and process design to EPC turnkey projects. We are committed to improving your gold recovery rate and ensuring return on investment through customized solutions.
Contact us today for free beneficiation trials and solution consultation!