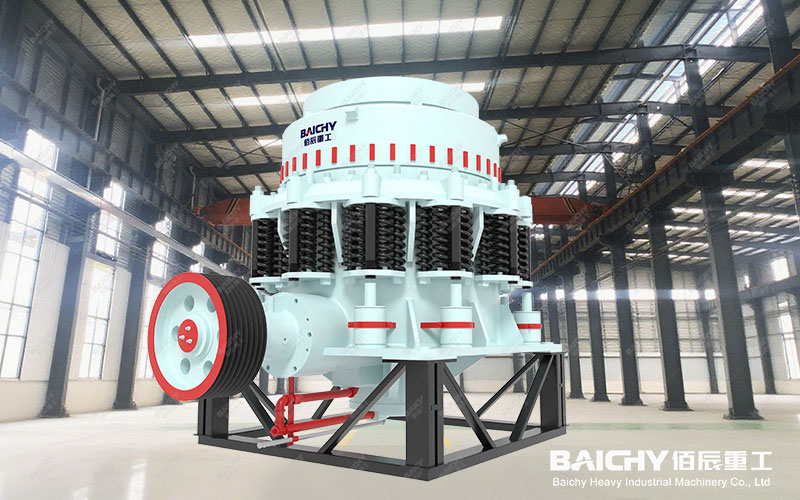
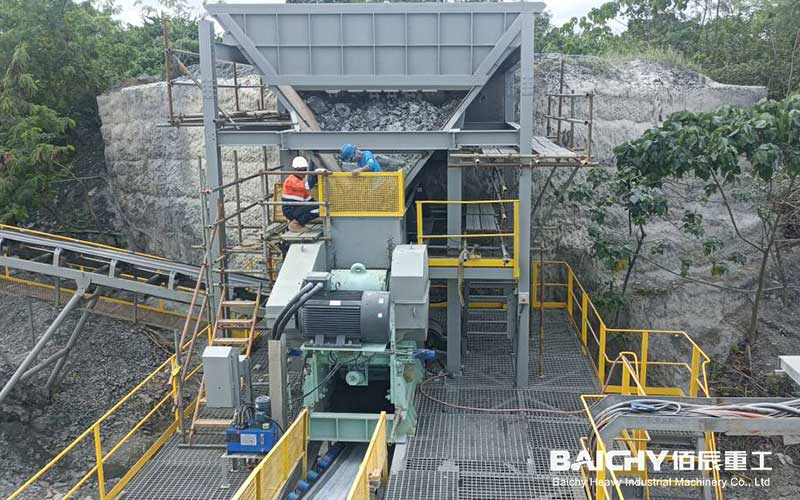
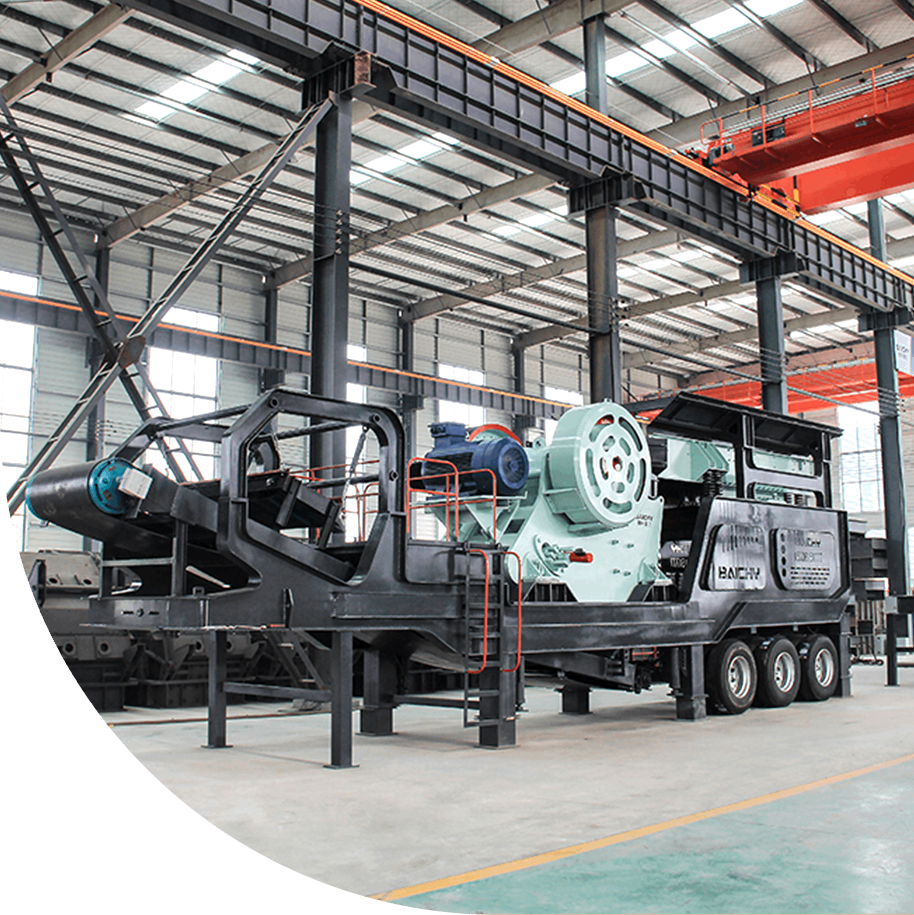
In the mining and aggregate processing industries, cone crushers are core equipment for the secondary and tertiary crushing stages. Their efficient and stable operation is directly related to the profitability of the entire production line. For equipment managers, maintenance engineers, and procurement personnel, a clear and comprehensive cone crusher parts list is not only a maintenance roadmap but also crucial for controlling costs and ensuring production.
This article provides a detailed parts breakdown guide, going beyond simple name lists to delve into the functions and interactions of major assemblies and wearing parts, as well as key maintenance and replacement points.
1. Core Assembly Components: The "Skeleton" and "Heart" of the Equipment
These components form the backbone of the cone crusher and typically have a long lifespan, but any damage can result in significant repair costs and downtime.
1. Mainframe: The foundation of the equipment, supporting all other components. It requires exceptional strength and stability.
2. Eccentric Sleeve Assembly: This is the "heart" of the cone crusher. The motor's power, through the transmission, rotates the eccentric sleeve, which in turn drives the moving cone in a oscillating motion, achieving the crushing function. This is one of the equipment's most sophisticated components.
3. Moving Cone Assembly: Consists of the main shaft, moving cone body, and the crushing wall (moving cone liner) mounted on it. It is the core component that directly performs the crushing action.
4. Fixed Cone Assembly (Adjustment Ring): Consists of the adjustment ring and the crushing wall (fixed cone liner) mounted on it. Together with the moving cone, it forms the crushing chamber. Adjusting the fixed cone height using hydraulic or screw mechanisms controls the output particle size.

II. Key Wear Parts List: The Focus of Maintenance
These parts require regular replacement due to normal wear and tear and are a key component of spare parts inventory management.
| Component Name | Function | Replacement Cycle Reference | Maintenance Points |
| Crushing Wall (Mooring Cone Liner) | Fixed to the moving cone, in direct contact with the material | 500-800 hours (depending on material hardness) | Replace with the mortar wall and check for secure tightening. |
| Mortar Wall (Cone Liner) | Fixed to the cone, forms the crushing chamber with the crushing wall | 500-800 hours (depending on material hardness) | Same as above, check the tightness of the U-bolts. |
| Liner (Frame Bushing) | Protects the contact surface between the main frame and the eccentric sleeve | Long, requires regular inspection | Prevents excessive wear that could damage the eccentric sleeve or main frame. |
| Wear-Resistant Parts | Located in locations such as the feed port and hopper | Based on wear | Regularly inspect to prevent material from eroding the equipment. |
III. Transmission and Hydraulic System Components: The Equipment's "Neural Network"
1. Transmission System: Includes pulleys, V-belts, couplings, etc., responsible for power transmission. Regularly inspect the belt tension and wear.
2. Hydraulic System: The "brain" of a modern cone crusher. It primarily includes the hydraulic station, cylinder, locking cylinder, and accumulator. It is responsible for iron-pass protection, discharge opening adjustment, and hydraulic locking. Hydraulic oil cleanliness is crucial for reliable operation of this system.
3. Dust Seal Assembly: This prevents dust from entering the lubrication system and protects precision components such as the eccentric sleeve and spherical bearing. Seal failure can lead to lubricant contamination and serious component damage, requiring careful attention.
IV. How to Use This Checklist for Scientific Maintenance?
• Establish a Spare Parts File: All equipment parts are numbered and filed according to the list for easy management.
• Develop an Inspection Plan: Develop a daily and regular inspection schedule for wearing parts, recording wear data.
• Scientific Inventory Planning: Based on the average lifespan and procurement cycle of wearing parts, set a safety stock level to avoid downtime due to lack of spare parts or overstocking.
• Train the Maintenance Team: Ensure team members are familiar with the names, functions, and replacement procedures of key components. A comprehensive cone crusher parts list is the cornerstone of predictive maintenance and improved Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE). By gaining a deep understanding of each component's function and maintenance requirements, you can shift from reactive maintenance to proactive management, maximizing equipment lifespan and ultimately creating greater value for your business.