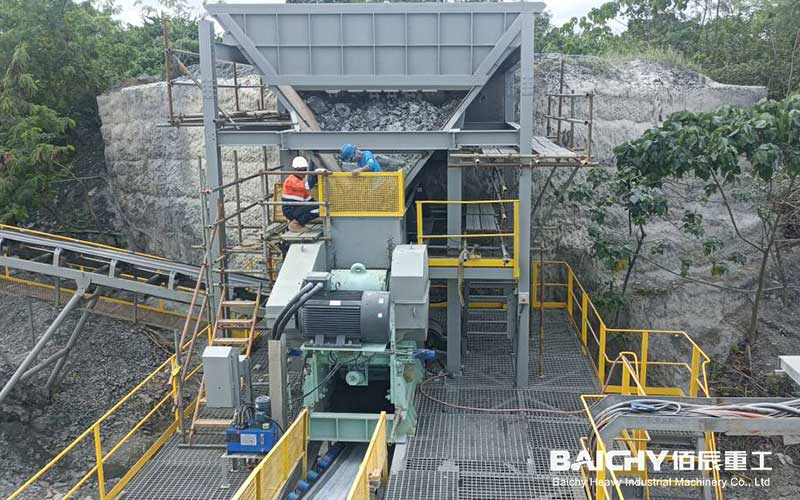
Jaw crusher vs gyratory crusher: Advantages and disadvantages comparison and selection guide
In the mining, building materials, metallurgy and other industries, the choice of coarse crushing equipment directly affects production efficiency and cost. Jaw crusher and gyratory crusher are two common primary crushing equipment, but they have significant differences in structure, capacity, energy consumption, etc. This article will compare the advantages and disadvantages of the two from multiple dimensions to help you choose the most suitable crusher.
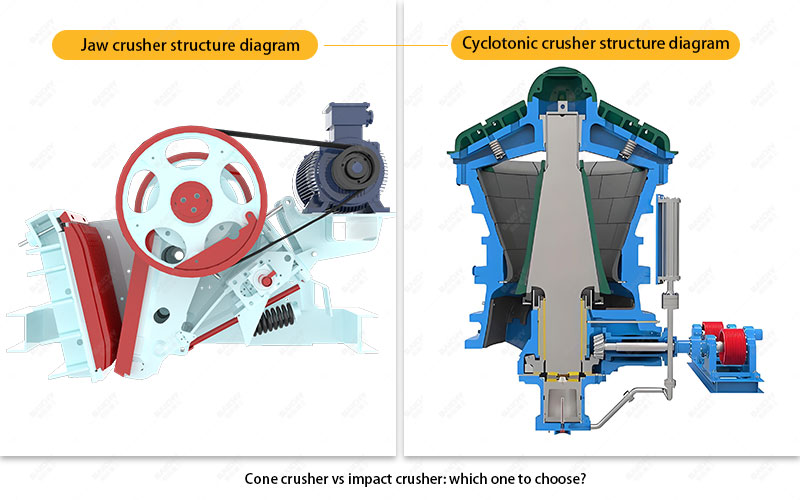
Working principle comparison
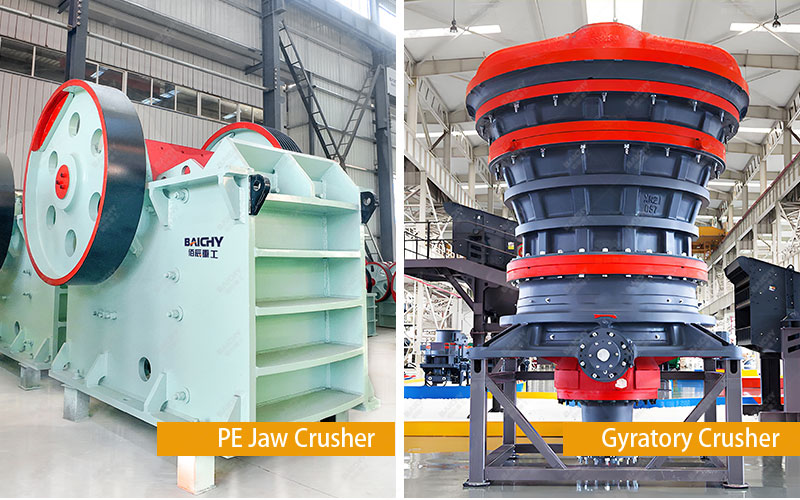
1. Jaw crusher
• Crushing method: The movable jaw and the fixed jaw periodically squeeze the material to achieve crushing.
• Applicable materials: medium and high hardness ores (such as granite, basalt), construction waste, etc.
• Feed particle size: ≤1500mm (depending on the model).
• Discharge particle size: 10-350mm (adjustable).
Advantages:
✔ Simple structure, easy maintenance
✔ Low investment cost
✔ Suitable for small and medium-sized production lines
Disadvantages:
✘ Relatively small crushing ratio (3-5)
✘ Low output, high unit energy consumption
✘ Jaw plate wears quickly and needs to be replaced regularly
2. Gyratory crusher
• Crushing method: The moving cone performs a swinging motion driven by the eccentric sleeve to squeeze and crush the material.
• Applicable materials: high-hardness ores (such as iron ore, copper ore), large quarries.
• Feed particle size: ≤2000mm (depending on the model).
• Discharge particle size: 50-300mm (adjustable).
Advantages:
✔ Large crushing ratio (6-8), high output
✔ Low unit energy consumption, suitable for large-scale production
✔ Long lining life, low maintenance cost
Disadvantages:
✘ Complex equipment, high initial investment
✘ High installation requirements, professional debugging required
✘ Sensitive to material moisture, easy to clog

Key performance comparison
| Comparison items | Jaw crusher | Gyratory crusher |
| Crushing ratio | 3-5 | 6-8 |
| Processing capacity | 50-1500 t/h | 500-8000 t/h |
| Energy consumption | High | Low |
| Equipment cost | Low | High |
| Maintenance difficulty | Simple | Complex |
| Applicable scale | Small and medium | Large |
How to choose? Selection suggestions
1. When to choose a jaw crusher
✔ Limited budget, low initial investment
✔ Small and medium-sized production lines, low output requirements
✔ High material hardness, but small feed size
✔ Limited space, need flexible movement
2. When to choose a gyratory crusher
✔ Large mines or quarries, high output requirements
✔ Pursuit of low long-term operating costs (energy consumption, maintenance)
✔ Large feed size, high crushing ratio required
✔ Stable production line, can afford high initial investment
Which is better?
• Jaw crushers are more suitable for small and medium-sized projects with limited budgets, simple maintenance, but low output and energy efficiency.
• Gyratory crushers are suitable for large-scale, high-output requirements, with lower long-term operating costs, but high initial investment.
The final choice depends on your production scale, budget and material characteristics. If you are still unsure, it is recommended to consult a professional crushing equipment supplier to customize a solution according to specific needs.
Further reading:
Application Guide And Maintenance Guide Of PEX Fine Jaw Crusher In Production Line