Jaw crusher is a coarse crushing equipment widely used in mining, building materials, metallurgy, and other industries. It is favored for its simple structure, large crushing ratio, and stable operation. This article will analyze the working principle of the jaw crusher in detail, including the core contents such as the movement mode of the movable jaw, the calculation of the crushing ratio, the eccentric shaft driving mechanism, and attach a structural diagram and workflow analysis to help users deeply understand its operating mechanism.
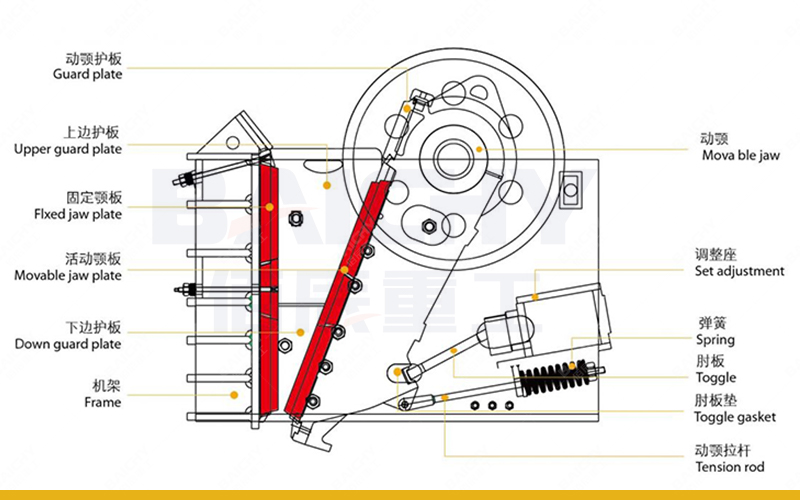
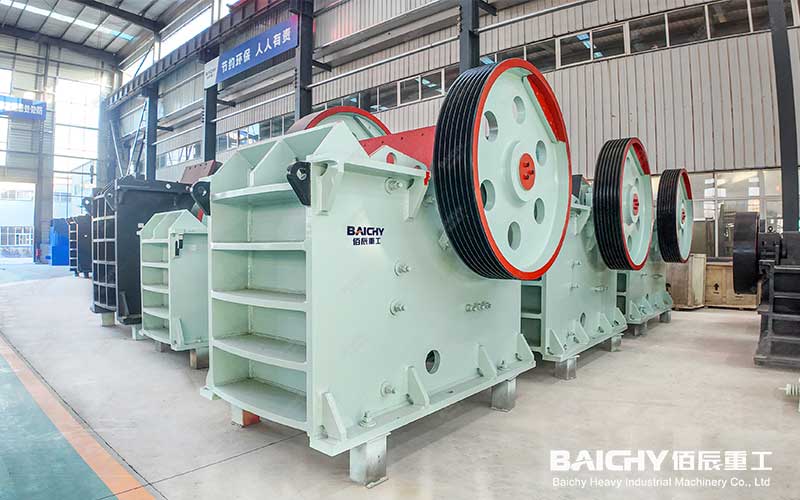
1. Basic structure of a jaw crusher
The jaw crusher is mainly composed of the following components:
• Frame: Supports the entire equipment and withstands the crushing force.
• Moving jaw and fixed jaw: The movable jaw swings periodically and forms an extrusion crushing chamber with the fixed jaw.
• Eccentric shaft: Drives the movable jaw to reciprocate and is the core transmission component.
• Adjustment device: Controls the size of the discharge port and adjusts the crushing ratio.
• Safety device (such as a toggle plate): protects the machine from damage when overloaded.
2. Working principle of jaw crusher
2.1 Movement mode of movable jaw (key principle)
When the jaw crusher is working, the motor drives the eccentric shaft to rotate through the pulley, driving the movable jaw to doa periodic reciprocating motion:
• Forward (extrusion) stage: The movable jaw approaches the fixed jaw, and the material is squeezed and crushed.
• Reverse (discharge) stage: the movable jaw moves away from the fixed jaw, and the crushed material is discharged under the action of gravity.
• This "extrusion-release" cycle allows the material to be continuously crushed until the required particle size is reached.
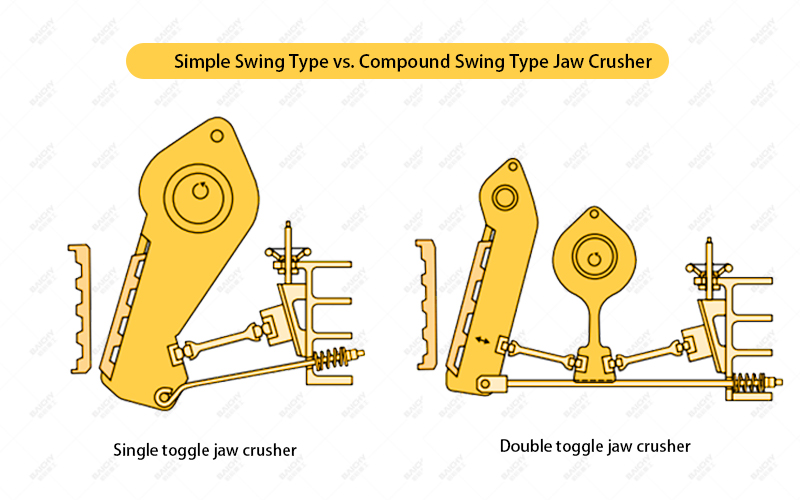
2.2 Simple swing type vs. compound swing type jaw crusher
| Comparison items | Simple swing type jaw crusher | Compound swing type jaw crusher |
| Moving jaw movement | Simple swing (arc trajectory) | Complex swing (elliptical trajectory) |
| Crushing efficiency | Lower | Higher (moving jaw has up and down movement, enhanced crushing) |
| Applicable scenarios | Coarse crushing in large mines | Small and medium-sized crushing, sand and gravel aggregates |
3. Application and maintenance of jaw crushers
3.1 Applicable materials
• High-hardness ore (such as granite, basalt)
• Construction waste (concrete, bricks)
• Metallurgical slag (iron ore, copper ore)
3.2 Common faults and solutions
| Fault phenomenon | Possible causes | Solutions |
| Large machine vibration | Loose anchor bolts | Tighten bolts and check foundation |
| Uneven discharge particle size | Wear of jaw plate | Replace jaw plate or adjust discharge port |
| Bearing overheating | Insufficient lubrication or impurities entering | Clean the bearings and replace the lubricating oil |

The jaw crusher achieves material crushing through the reciprocating extrusion motion of the moving jaw, and has the advantages of simple structure, strong adaptability, and easy maintenance. Choosing a suitable jaw crusher (such as a compound swing type or a simple swing type) and maintaining it correctly can greatly improve production efficiency.
For more detailed technical parameters or selection suggestions, please consult our engineers!