Magnetic Separation in Mining and Mineral Processing
In iron ore beneficiation production lines, magnetic separators are not merely equipment, but rather the core efficiency-enhancing engine of the entire process. Below, we will analyze from a technical perspective how magnetic separators play an irreplaceable role in iron ore beneficiation production lines.
The Strategic Positioning of Magnetic Separators in Iron Ore Beneficiation
Why is Magnetic Separation the Preferred Method for Iron Ore Beneficiation?
Iron ores, especially magnetite and hematite, exhibit significant differences in magnetic properties. Magnetic separators utilize this natural characteristic to achieve efficient, low-cost, and environmentally friendly separation. Compared to flotation and gravity separation, magnetic separation requires no complex reagents, has lower operating costs, and is easier to automate, making it the technological cornerstone of modern iron ore beneficiation.
The Multi-Stage Role in the Production Line
Magnetic separators in iron ore beneficiation are not operating in a single-point manner, but rather are strategically deployed across the entire process and multiple stages, forming a closed-loop separation system to maximize value extraction.
In-depth Application in Stages Throughout the Entire Process
Stage 1: Pre-selection and Waste Disposal (After Crushing, Before Grinding)
• Objective: To discard low-grade waste rock and surrounding rock before the ore enters the energy-intensive grinding process.
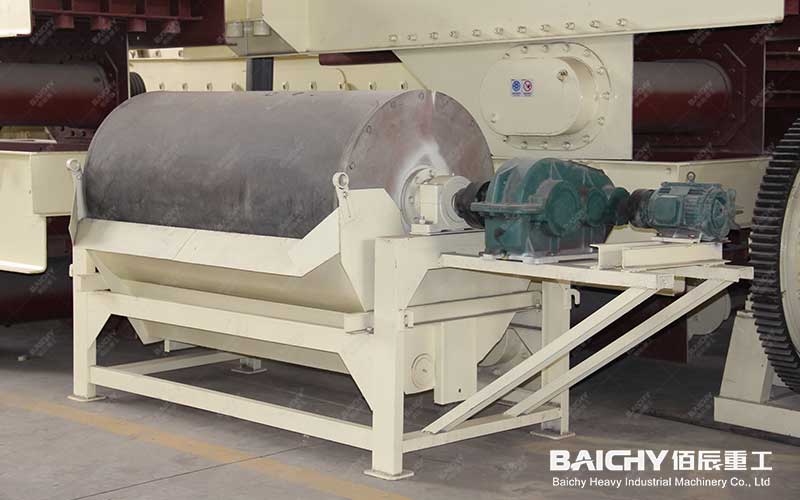
• Equipment Application: Large-scale dry magnetic separator or permanent magnet drum.
• Value Proposition:
1. Reduced Grinding Load: Discarding 20%-30% of waste rock directly reduces the amount fed into the mill.
2. Significant Energy Savings: Mill power consumption can be reduced by more than 20%, resulting in a significant decrease in cost per ton of ore.
3. Increased Feed Grade: Providing finer raw materials for subsequent processes, improving overall efficiency.
Stage 2: Stage Grinding and Stage Separation (Core Separation)
This is the main battleground where the magnetic separator plays a core role, typically employing a cyclical process of multi-stage grinding - multi-stage magnetic separation.
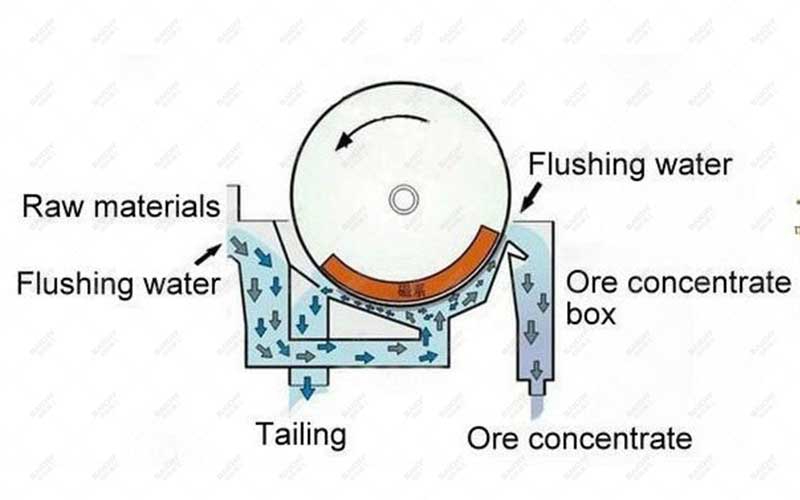
• Rough Grinding and Concentration: After primary grinding, a wet permanent magnet drum separator (CTS) is used for roughing to quickly obtain a rough concentrate and discard a large amount of tailings.
• Regrinding and Concentration: The rough concentrate enters a second-stage grinding process for further liberation, followed by multiple fine separations using magnetic separators.
• Technical Highlights: A combination of magnetic separators with different tank structures (co-current, semi-counter-current, and counter-current) is used to address different particle size and grade requirements, ensuring a balance between high recovery rate and high concentrate grade.
Third Stage: Tailings Scavenging and Resource Recovery
• Objective: To scavenger the tailings from the main process to maximize metal recovery.
• Equipment Application: Scavenging magnetic separators are installed at the overflow points of tailings troughs or thickeners.
• Value Proposition: Residual magnetic iron minerals in the tailings can be recovered, increasing the overall recovery rate by 1%-3%, resulting in significant long-term operational benefits.
Working-principle-of-magnetic-separator
Magnetic Separation Processes for Different Types of Iron Ore
1. Single Magnetite Beneficiation
• Process Flow: Stage grinding - stage magnetic separation. This is the most classic and efficient process.
• Core Equipment: CT series permanent magnet drum magnetic separator. Due to its stable magnetic field strength, lack of excitation power supply, and energy efficiency, it has become the dominant technology. By connecting multiple units in series, a step-by-step increase in concentrate grade can be achieved (e.g., from 55% to over 68%).
2. Mixed Type (Magnetite-Hematite) or Weakly Magnetic Iron Ore Beneficiation
• Process Challenge: Weakly magnetic minerals such as hematite require a strong magnetic field for recovery.
• Solutions:
◦ Solution A: Magnetized roasting - magnetic separation. First, convert hematite into magnetite, then separate it using a conventional magnetic separator.
◦ Solution B: High-intensity magnetic separation process. High-gradient magnetic separators or electromagnetic high-intensity magnetic separators are directly used, with magnetic field strengths exceeding 1.0T, effectively recovering fine-grained weakly magnetic iron minerals.
3. Reprocessing of Ultra-Lean Iron Ore and Tailings
• Core Process: Discard as early as possible, recover as much as possible.
• Equipment Application: High-efficiency dry magnetic separators are used for pre-discarding waste after ultrafine crushing; in tailings reprocessing, a combined process of concentration-high-frequency desliming-high-gradient magnetic separation is used to extract value from waste.
Our Solutions and Core Advantages
With 20 years of experience, we provide global iron ore customers with not only equipment, but also customized efficiency-enhancing solutions.
Technical Equipment Advantages
1. High-Performance Magnetic System: High-grade neodymium iron boron magnets are used, with optimized magnetic circuit design to ensure high field strength, deep penetration, long lifespan, and industry-leading recovery rates.
2. Wear-resistant and Corrosion-resistant Design: The drum is made of thickened stainless steel or high-polymer composite coating, and key parts of the tank are inlaid with ceramic or rubber, adapting to harsh slurry environments and doubling the maintenance cycle.
3. Intelligent Control Interface: The equipment has reserved sensor interfaces, which can be linked with online grade analyzers and automatic ballers, laying the foundation for realizing a smart beneficiation plant.
Process Design Advantages
We provide a one-stop service of magnetic separation test - process design - equipment selection. Through detailed ore beneficiation tests, we determine the most economical grinding fineness, magnetic field strength, and process structure for you, avoiding the predicament of oversized equipment or insufficient capacity.
Successful Application Cases
• Case: Upgrading Project of a Large Iron Mine Beneficiation Plant in Hebei Province
◦ Original Problem: The original production line's magnetic separator was aging, with concentrate grade hovering around 65% and tailings grade as high as 12%, resulting in serious resource waste.
◦ Our Solution: Utilizing a new process of two-stage closed-circuit crushing + high-pressure roller mill - staged magnetic separation, all core equipment has been replaced with our large-scale CT series permanent magnet separators and high-gradient scavenging machines.
◦ Results: Concentrate grade stabilized above 68.5%, tailings grade decreased to below 8%, annual concentrate production increased by 150,000 tons, and investment payback period was less than 14 months.
Recommended Related Process Components
• Feed Preparation: Equipped with a frequency converter-controlled vibrating feeder to ensure uniform and stable feeding, a prerequisite for efficient magnetic separation.
• Classification Optimization: Closed-circuit grinding is constructed with hydrocyclones to strictly control the particle size of the magnetic separation feed, optimizing the separation effect.
• Dewatering System: For the magnetically separated concentrate, we recommend using our high-efficiency thickener + ceramic filter combination to achieve efficient dewatering and reduce transportation costs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: How to improve the magnetic separation recovery rate for refractory iron ore with finely disseminated particles?
A1: The key is to achieve complete mineral liberation and use targeted magnetic separation equipment.
Recommendations:
1) Adopt a multi-stage grinding and separation process of re-grinding and re-selection;
2) Use a high-gradient magnetic separator in the selection stage, which has a high background field strength and the magnetically focused medium can capture fine-grained magnetic minerals;
3) Add pulsating or high-frequency vibration to the scavenging stage to reduce mechanical inclusions.
Q2: Is a higher magnetic field strength in the magnetic separator always better?
A2: Not necessarily. The magnetic field strength needs to be precisely matched with the ore's magnetic properties, particle size, and grade requirements. Excessive field strength can cause non-magnetic gangue to be mechanically entrained, reducing concentrate grade and increasing energy consumption. Our engineers will conduct experiments to determine the optimal field strength range for you that is both economical and efficient.
Q3: How can the magnetic separation process be made intelligent in an iron ore beneficiation production line?
A3: The core is a closed loop of sensing-analysis-optimization.
1) Sensing: Online grade analyzers are installed in the magnetic separation feed, concentrate, and tailings pipelines to monitor indicators in real time;
2) Analysis: Data is analyzed through an expert system to determine operating conditions;
3) Optimization: The feed rate, drum speed, or flushing water volume is automatically adjusted. Our new magnetic separator has a reserved standard interface, supporting seamless integration with intelligent beneficiation plant systems.