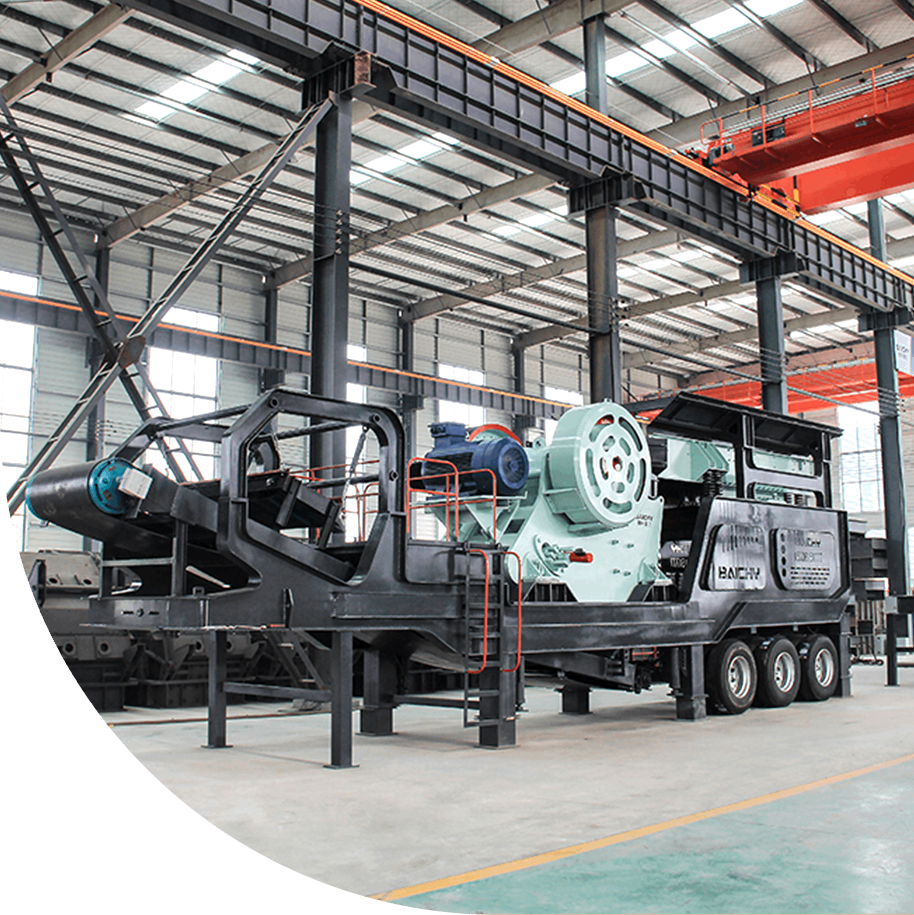
Sudan, leveraging its abundant gypsum resources and advantageous geographical location, is actively promoting the development of the gypsum calcination (calcium sulfate) industry. Initial manufacturing costs are a core aspect of project feasibility assessment when establishing a gypsum calcination plant.
This article provides an in-depth analysis of the initial manufacturing costs of calcined gypsum production lines with daily capacities of 600 tons and 900 tons, offering practical reference for investors and planners.
Initial Manufacturing Cost Composition
The initial manufacturing costs of a gypsum calcination production line mainly include equipment procurement, site construction, infrastructure support, technical services, and initial operational preparation. The following estimates for two capacity scales are based on typical projects (Note: Actual costs are affected by factors such as equipment selection, automation level, and local prices; this data is for reference only):
1. 600-ton-per-day production line
• Equipment Costs: Investment in core equipment such as the calcining furnace, crusher, and grinding mill is approximately US$3-4.5 million.
• Site and Buildings: Construction costs for plant, warehouse, and infrastructure are approximately US$1.5-2.5 million. • Installation and Commissioning: Includes equipment installation, system integration, and technical services, costing approximately US$800,000-1,200,000.
• Total Initial Cost: Approximately US$5,300,000-8,200,000.
2. 900-ton/day Production Line
• Equipment Costs: Due to the increased scale, higher-specification equipment is required, with an investment of approximately US$4,500,000-6,500,000.
• Site and Buildings: Requires a larger site area, with construction costs of approximately US$2,000,000-3,500,000.
• Installation and Commissioning: Increased complexity, costing approximately US$1,000,000-1,500,000.
• Total Initial Cost: Approximately US$7,500,000-11,500,000.
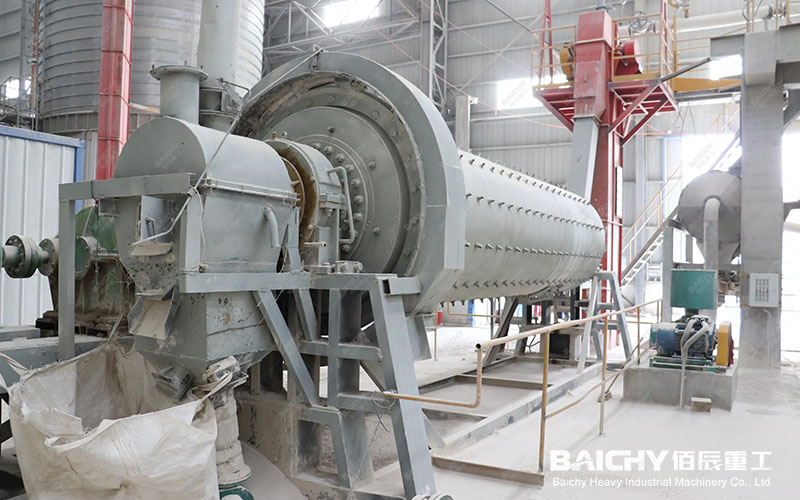

Cost Influencing Factors
• Technology Selection: Different calcination technologies, such as rotary kilns or fluidized bed furnaces, result in significant cost differences.
• Localization: Local equipment supply and labor costs in Oman can reduce some expenses.
• Environmental Protection and Energy: Budget must be allocated to meet environmental standards, and energy (such as natural gas) supply solutions must be optimized. Recommendations and Outlook
When investing in a gypsum calcination plant in Oman, it is recommended to precisely control costs through a detailed feasibility study. Prioritize modular equipment to shorten the construction cycle and fully utilize local policy support. With the growing global demand for gypsum in the construction industry, medium-to-high production lines of 600 tons and 900 tons offer excellent economic return potential.
For a more precise cost plan, please contact our professional team for an on-site assessment!