A crusher is a mechanical device used to break large solid materials into smaller particles by mechanical force. It is widely used in mining, metallurgy, building materials, chemicals, environmental protection, and other industries. The following is a detailed introduction to crushers:
Main types of crushers
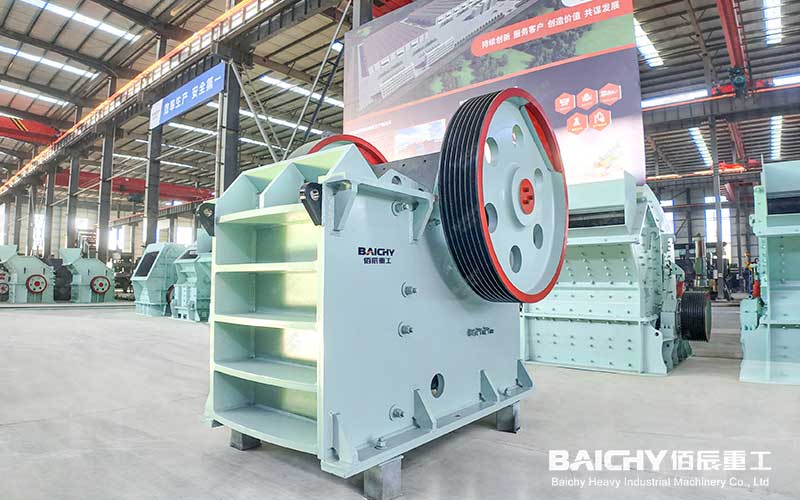

PE Jaw Crusher
1. Jaw crusher
Principle: Crushing materials by periodic extrusion movement of the movable jaw and the fixed jaw.
Features: Simple structure, large processing capacity, suitable for coarse crushing of high-hardness materials (such as granite, ore).
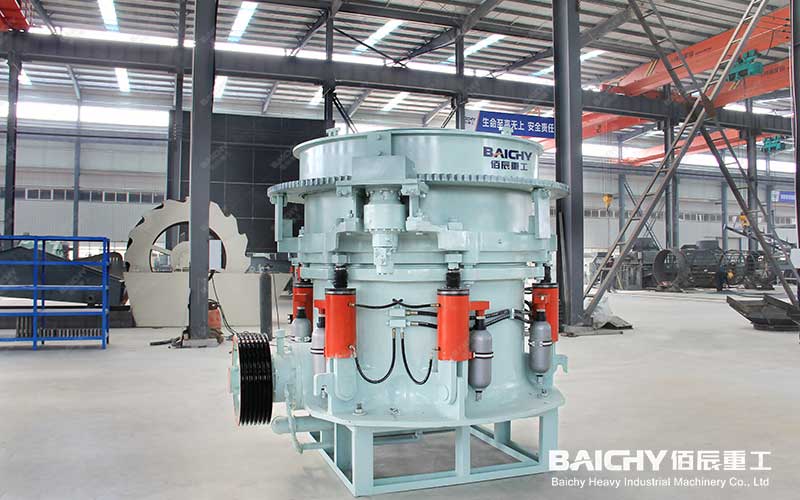

Hydraulic Cone Crusher
2. Cone crusher
Principle: Crushing materials by the extrusion and bending between the cone of the swinging motion and the fixed cone wall.
Features: Medium and fine crushing equipment, large crushing ratio, suitable for high-hardness materials, stable operation.
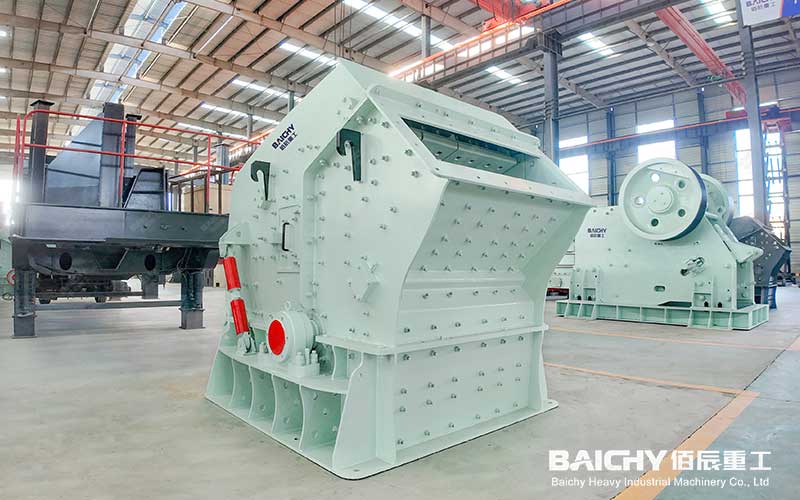

PFW Impact Crusher
3. Impact crusher
Principle: The high-speed rotating rotor drives the hammer to hit the material and crush it by impact force.
Features: The finished particles have good shape, suitable for medium-hardness materials (such as limestone, concrete), but are easy to wear.
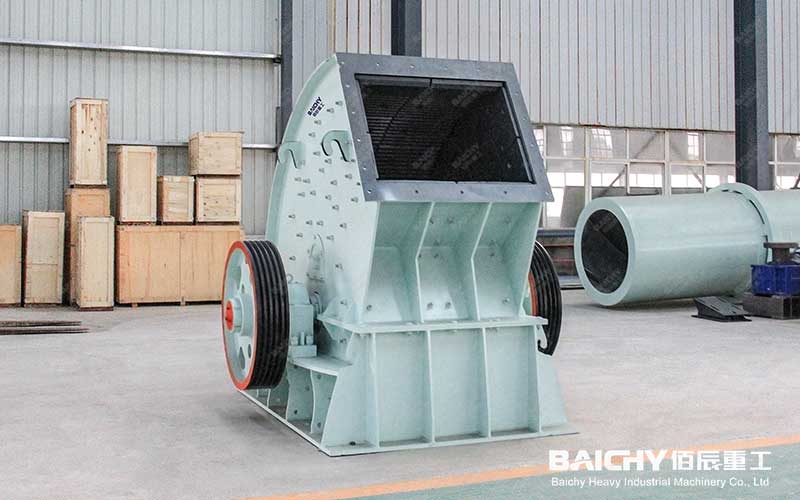

Heavy Hammer Crusher
4. Heavy Hammer crusher
Principle: By hitting the material with a high-speed rotating hammer, coarse and medium crushing can be completed simultaneously.
Features: Simple structure, but only suitable for low-hardness, brittle materials (such as coal, gypsum).
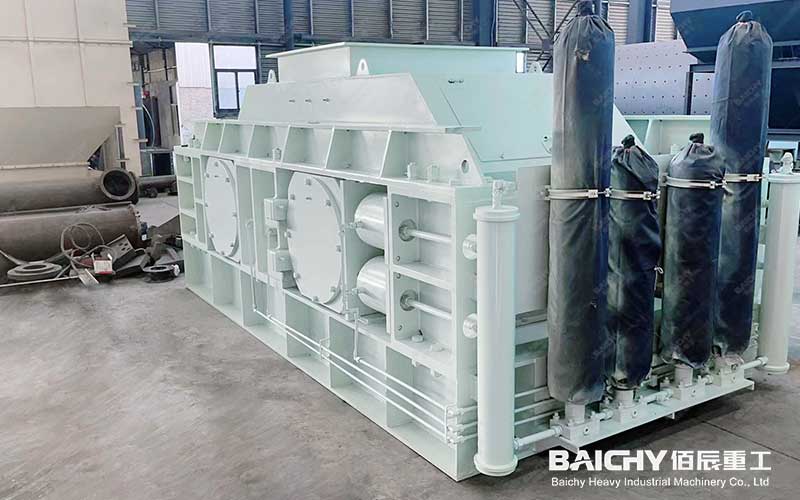

Double Roller Crusher
5. Double Roller crusher
Principle: Two rollers rotating in opposite directions squeeze the material, suitable for fine crushing or sand making.
Features: Less over-crushing, but low processing capacity.
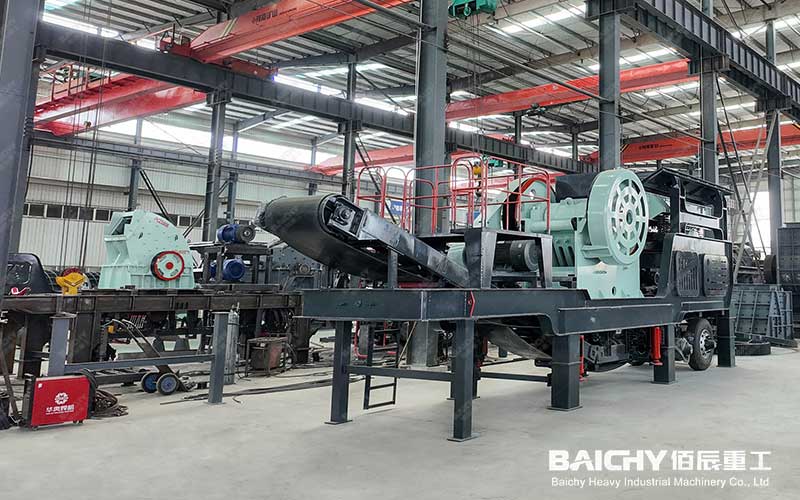

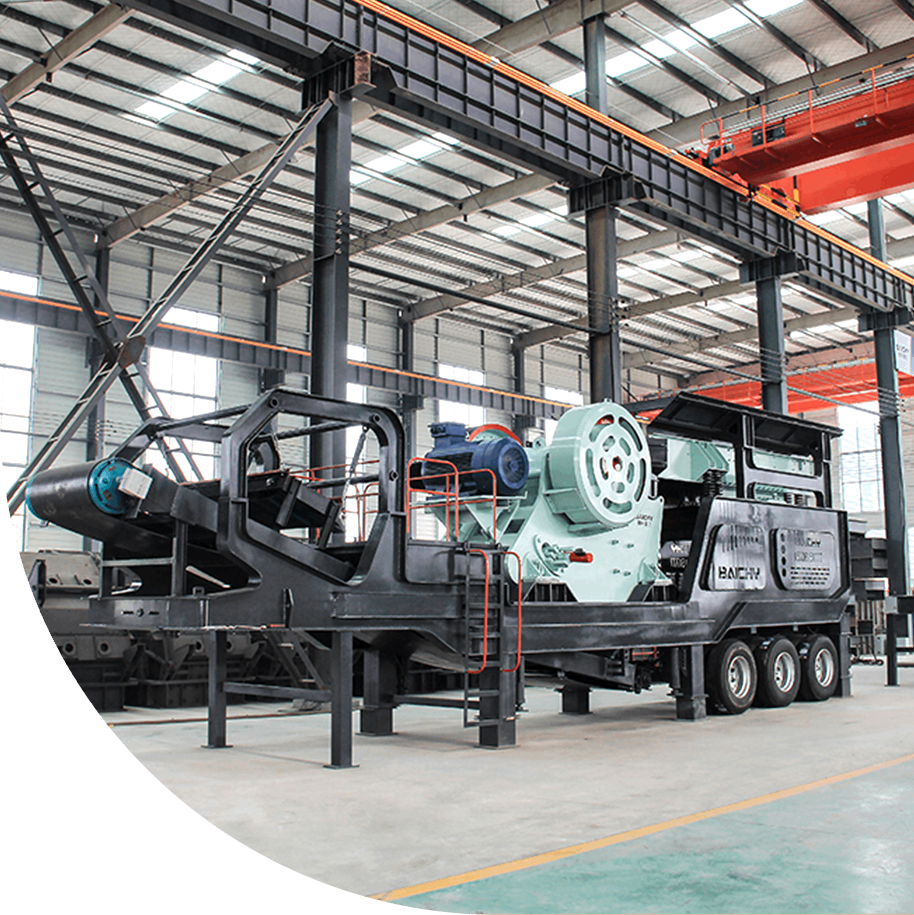
Mobile Jaw Crusher
6. Mobile Jaw Crusher
Features: Integrates feeding, crushing, and transportation, and is flexibly used in scenes such as construction waste treatment and open-pit mining.
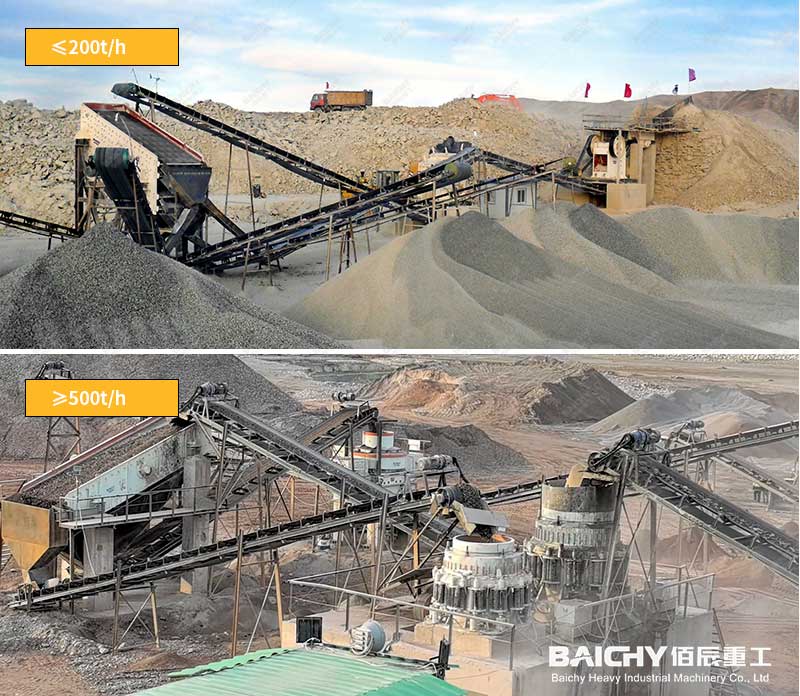

Stone Crushing Plant
Key factors for selecting a crusher
1. Material properties
Hardness: For high hardness (such as granite), choose a jaw crusher and a cone crusher; for medium and low hardness (limestone), choose an impact crusher.
Humidity/viscosity: Wet materials require an anti-blocking design (such as a hammer crusher).
Impurity content: Metal impurities require an iron remover.
2. Production requirements
Production capacity: jaw crusher (50-1500t/h) > impact crusher (30-800t/h) > cone crusher (12-700t/h).
Finished product size: When multi-stage crushing is required, a combination of coarse crushing + medium and fine crushing (such as jaw crusher + cone crusher).
3. Economic efficiency
Investment cost: hammer crusher < jaw crusher < impact crusher < cone crusher < mobile crusher.
Maintenance cost: impact crusher (frequent replacement of wearing parts) > cone crusher (maintenance of precision parts) > jaw crusher (simple structure).
Frequently asked questions
Q: How to choose between an impact crusher and a cone crusher?
A: If you pursue particle shape (such as commercial concrete aggregate) and the material is not hard, choose an impact crusher; if you crush high hardness materials and need high production capacity, choose a cone crusher.
Q: Is the mobile crusher suitable for long-term use?
A: It is suitable for short-term or dispersed operations. For long-term fixed production, it is recommended to choose a fixed production line (low cost and high stability).
Q: How to reduce the wear of the hammer crusher?
A: Control the hardness of the material (Mohs hardness ≤ 4), feed evenly, and regularly turn over or replace the hammer head.